As the population ages, the need for long-term care services is steadily increasing. Long-term care insurance, a specialized type of coverage, can provide financial protection against the potentially exorbitant costs of these services. This guide delves into the complex world of long-term care insurance companies, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your future care.
Choosing the right long-term care insurance company is a crucial step in safeguarding your financial well-being and ensuring access to quality care when you need it most. This guide explores key considerations for selecting a company, understanding policy features, and navigating the application process. We also delve into alternative options for financing long-term care, address common misconceptions, and provide valuable resources to empower consumers.
Understanding Long-Term Care Insurance
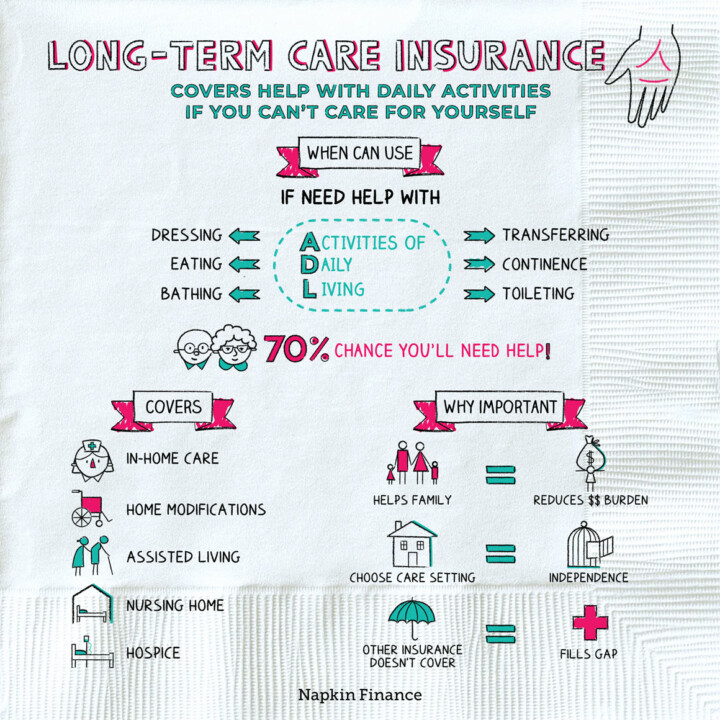
Long-term care insurance is a type of insurance policy that helps pay for the costs of long-term care services, such as assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs) and skilled nursing care. It can be a valuable asset for individuals who want to protect their financial resources and ensure they have access to quality care if they need it.
Types of Long-Term Care Services Covered
Long-term care insurance policies typically cover a range of services, including:
- Assistance with ADLs: This includes help with tasks such as bathing, dressing, eating, toileting, and transferring.
- Skilled Nursing Care: This involves providing medical care, such as wound care, medication management, and physical therapy.
- Homemaker Services: These services provide help with light housekeeping, meal preparation, and laundry.
- Adult Day Care: This type of care provides supervision and support for individuals who need assistance during the day.
- Respite Care: This provides temporary care for individuals with long-term care needs, allowing their caregivers to take a break.
Costs Associated with Long-Term Care
The cost of long-term care can vary significantly depending on the type of care needed, the location, and the level of care provided. According to the Genworth Cost of Care Survey, the national median annual cost for a private room in a nursing home in 2023 is $108,405. Assisted living facilities have a median annual cost of $55,000. Homemaker services can range from $20 to $40 per hour.
Situations Where Long-Term Care Insurance is Beneficial
Long-term care insurance can be beneficial in several situations, including:
- Individuals with a family history of chronic illness: If an individual has a family history of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, or heart disease, they may be at a higher risk of needing long-term care.
- Individuals who want to protect their assets: Long-term care can be very expensive, and without insurance, it can deplete an individual’s savings and assets.
- Individuals who want to ensure they have access to quality care: Long-term care insurance can provide peace of mind by ensuring that individuals have access to the care they need, regardless of their financial situation.
Key Considerations for Choosing a Company

Choosing the right long-term care insurance company is crucial, as it will be responsible for providing financial assistance for your future care needs. You need to consider various factors beyond just the cost of premiums. It’s essential to evaluate the financial stability, customer service, and policy features of different companies to make an informed decision.
Financial Stability
The financial stability of a long-term care insurance company is paramount. It ensures that the company will be able to pay your benefits when you need them. You can assess a company’s financial strength by looking at its ratings from independent agencies such as A.M. Best, Standard & Poor’s, and Moody’s. Companies with higher ratings, such as A+ or above, generally have a stronger financial track record and are more likely to remain solvent in the long term.
Customer Service
Customer service is a crucial aspect of long-term care insurance. You want to ensure that the company is responsive to your inquiries, handles claims efficiently, and provides clear and helpful information. You can research a company’s customer service by reading online reviews, checking with the Better Business Bureau, and contacting the company directly with questions.
Policy Features
Long-term care insurance policies vary significantly in their features, such as coverage amounts, benefit periods, and exclusions. It’s important to compare policies from different companies to find one that best meets your needs and budget.
Comparing Key Features of Leading Companies
| Company | Premium (Annual) | Maximum Benefit | Benefit Period | Exclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | $2,000 | $100,000 | 5 years | Cognitive impairment, mental illness |
| Company B | $2,500 | $150,000 | 10 years | Substance abuse, self-inflicted injuries |
| Company C | $1,800 | $80,000 | 3 years | Chronic conditions, pre-existing conditions |
Understanding Policy Features and Benefits
Long-term care insurance policies come with a variety of features and benefits that can significantly impact the overall cost and coverage. Understanding these features is crucial for choosing a policy that aligns with your individual needs and financial situation.
Benefit Period
The benefit period refers to the maximum length of time the policy will cover your long-term care expenses. It is typically measured in years or days. Common benefit periods range from 2 to 6 years, although some policies offer longer durations. The longer the benefit period, the higher the premium.
- Short benefit periods (e.g., 2 years) may be suitable for individuals who expect to need care for a shorter duration, or who have significant savings or other resources to cover long-term care expenses beyond the benefit period.
- Longer benefit periods (e.g., 5 or 6 years) provide greater financial security, but come with higher premiums. These policies are often recommended for individuals who are concerned about the possibility of needing care for an extended period or who have limited savings.
Daily Benefit Amount
The daily benefit amount represents the maximum amount the policy will pay per day for covered long-term care services. This amount should be sufficient to cover the cost of care in your area.
- Higher daily benefit amounts provide more financial protection, but result in higher premiums.
- Lower daily benefit amounts can reduce premiums, but may not fully cover the cost of care in some areas.
Inflation Protection
Inflation protection is a feature that helps protect your benefits from the effects of rising healthcare costs. Without inflation protection, the daily benefit amount will remain fixed throughout the policy’s duration, which could lead to a significant shortfall in coverage as healthcare costs increase.
- Compound inflation protection increases the daily benefit amount at a fixed rate each year, typically 3% or 5%. This provides the most robust protection against inflation.
- Simple inflation protection increases the daily benefit amount by a fixed percentage at the start of the policy term. This provides less protection against inflation than compound inflation protection, but may be more affordable.
- No inflation protection means the daily benefit amount will remain fixed throughout the policy’s duration. This option is typically the least expensive, but it exposes you to the risk of significant underfunding as healthcare costs rise.
Policy Limitations and Exclusions
It’s important to understand the limitations and exclusions of a long-term care insurance policy before you purchase it. These limitations can affect the coverage you receive and may limit the policy’s effectiveness in protecting your finances.
- Pre-existing conditions: Some policies may exclude coverage for certain pre-existing conditions.
- Waiting periods: There may be a waiting period before benefits are paid. This waiting period is typically 30 to 90 days.
- Benefit caps: Some policies may have a maximum benefit cap, which limits the total amount of benefits you can receive.
- Coverage exclusions: Policies may exclude certain types of care, such as experimental treatments or care provided in a hospital setting.
The Application and Underwriting Process
Applying for long-term care insurance involves a series of steps, from filling out an application to undergoing an underwriting process. Understanding these steps can help you prepare for the process and make informed decisions.
The Application Process
The application process for long-term care insurance begins with gathering information about your health, financial situation, and care needs. This information is crucial for the insurer to assess your risk and determine your premium.
- Gathering Information: The application form will typically ask for details about your health history, including any pre-existing conditions, current medications, and recent medical tests. You may also be asked about your family history of long-term care needs. Additionally, the insurer will want to know your age, occupation, and lifestyle.
- Financial Information: The application will also require information about your financial situation, such as your income, assets, and debt. This information helps the insurer assess your ability to afford the premiums.
- Care Needs: You will be asked to provide information about your current care needs, including any assistance you require with activities of daily living (ADLs). This information helps the insurer determine the level of coverage you may need.
The Underwriting Process
After you submit your application, the insurer will begin the underwriting process, which involves evaluating your health and financial information to assess your risk.
- Medical Review: The insurer will review your medical history and may request additional medical records from your doctor. This helps them assess your health and determine your risk of needing long-term care.
- Financial Assessment: The insurer will also review your financial information to ensure you can afford the premiums. This includes evaluating your income, assets, and debt.
- Risk Assessment: Based on your medical and financial information, the insurer will determine your risk of needing long-term care and calculate your premium.
Factors Influencing Eligibility and Premiums
Several factors can influence your eligibility for long-term care insurance and the premium you will pay.
- Age: Your age is a significant factor in determining your premium, as older individuals are more likely to need long-term care.
- Health: Your health history and current health status play a major role in underwriting. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or a family history of long-term care needs may face higher premiums.
- Lifestyle: Your lifestyle choices, such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption, can also influence your premium.
- Policy Features: The features of your policy, such as the benefit amount, daily benefit, and inflation protection, can also impact your premium.
Cost Considerations and Financial Planning
Long-term care insurance premiums can vary significantly, and understanding the factors that influence these costs is crucial for making informed decisions. This section delves into the key considerations for managing the cost of long-term care insurance and provides insights into integrating it into your overall financial planning.
Factors Influencing Long-Term Care Insurance Premiums
Several factors contribute to the cost of long-term care insurance premiums. Understanding these factors allows you to make informed decisions about coverage and manage costs effectively.
- Age: Premiums are typically higher for older individuals as they have a higher likelihood of needing long-term care.
- Health: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions may face higher premiums.
- Gender: Women generally pay higher premiums than men due to their longer life expectancy.
- Coverage Options: Premiums are influenced by the type and amount of coverage you choose, including the daily benefit amount, the length of coverage, and the benefit period.
- Location: Premiums can vary based on your state of residence, as the cost of long-term care services can differ significantly across geographic areas.
- Inflation Protection: Choosing inflation protection, which adjusts benefits over time to account for rising costs, will increase your premium.
- Company Financial Strength: Insurance companies with strong financial ratings generally offer more stable premiums.
Strategies for Managing the Cost of Long-Term Care Insurance
Managing the cost of long-term care insurance requires careful consideration and planning. Here are some strategies:
- Purchase Early: Purchasing long-term care insurance at a younger age can result in lower premiums, as you are less likely to need care immediately.
- Consider a Shorter Benefit Period: A shorter benefit period can lower your premiums. This might be suitable if you are concerned about the cost or believe you will not need long-term care for an extended period.
- Opt for a Lower Daily Benefit: A lower daily benefit can reduce premiums. However, ensure it aligns with your estimated long-term care costs.
- Evaluate Inflation Protection: While inflation protection is beneficial, it increases premiums. Carefully weigh the potential benefits against the additional cost.
- Shop Around: Compare quotes from multiple insurers to find the best rates and coverage options.
- Consider Health and Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and addressing pre-existing conditions can potentially improve your health and reduce premiums.
Incorporating Long-Term Care Insurance into Financial Planning
Integrating long-term care insurance into your financial planning requires a holistic approach:
- Assess Your Needs: Determine the potential need for long-term care based on your age, health, family history, and lifestyle.
- Estimate Costs: Research the estimated cost of long-term care in your area to determine the appropriate level of coverage.
- Consider Other Financial Resources: Evaluate your savings, investments, and other financial resources to determine the affordability of long-term care insurance.
- Consult with a Financial Advisor: A financial advisor can help you develop a comprehensive financial plan that incorporates long-term care insurance and other financial goals.
- Review Regularly: Regularly review your long-term care insurance policy and adjust it as needed to reflect changes in your health, financial situation, or long-term care needs.
Alternatives to Long-Term Care Insurance

While long-term care insurance provides financial protection against the high costs of long-term care, it’s not the only option available. Several alternatives exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to carefully consider your financial situation and long-term care needs.
Self-Funding
Self-funding involves saving enough money to cover future long-term care expenses. This approach can be appealing for individuals who are financially secure and believe they can save enough to cover their potential needs.
- Advantages:
- No premiums or policy limitations.
- Complete control over how your funds are used.
- Potential for tax-advantaged savings accounts like a Health Savings Account (HSA) or a traditional IRA.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires significant savings and disciplined financial planning.
- Risk of outliving your savings, especially with rising healthcare costs.
- No guarantee of covering all potential long-term care expenses.
For example, a couple in their 60s with a combined income of $200,000 and a net worth of $1 million might consider self-funding, assuming they can save a substantial portion of their income and invest wisely to achieve their long-term care goals. However, they need to be prepared for potential market fluctuations and the possibility of outliving their savings.
Medicaid
Medicaid, a government-funded program, provides financial assistance for long-term care services to low-income individuals and families.
- Advantages:
- Covers a wide range of long-term care services, including nursing home care, home health care, and adult day care.
- No premiums or deductibles.
- Disadvantages:
- Strict eligibility requirements, including income and asset limitations.
- Limited choice of providers and care settings.
- Potential for long wait times for services.
For individuals with limited financial resources, Medicaid can be a lifeline, providing access to essential long-term care services. However, it’s crucial to understand the eligibility requirements and the potential limitations of Medicaid coverage.
Reverse Mortgages
A reverse mortgage allows homeowners aged 62 or older to borrow against the equity in their homes without making monthly payments.
- Advantages:
- Provides access to a lump sum of cash or a monthly payment stream.
- No monthly mortgage payments.
- Can be used to cover long-term care expenses.
- Disadvantages:
- Interest rates can be higher than traditional mortgages.
- Borrowing against your home equity can reduce the inheritance for your heirs.
- You must continue to pay property taxes and homeowner’s insurance.
A couple with a paid-off home worth $500,000 might consider a reverse mortgage to access funds for long-term care expenses. However, they need to weigh the potential benefits against the risks, including the possibility of owing more than the home is worth if its value declines.
Common Misconceptions and Concerns
Long-term care insurance, like any financial product, is often subject to misunderstandings and concerns. It’s crucial to approach this decision with a clear understanding of its intricacies and potential drawbacks. This section aims to address common misconceptions and concerns, empowering you to make informed choices.
Policy Changes and Rising Premiums
Policy changes and premium increases are potential concerns for long-term care insurance. While policies are designed to provide coverage for a defined period, insurers may adjust their terms and conditions over time.
This could involve changes to benefits, coverage limitations, or premium adjustments.
It’s essential to understand that long-term care insurance is a long-term commitment, and premium increases are a possibility.
Here are some key considerations:
- Review Policy Details: Carefully examine your policy’s terms and conditions, including provisions related to premium adjustments. Understand the factors that could influence future premium increases.
- Consider Guaranteed Renewable Policies: These policies offer protection against premium increases based on your age or health. However, they may come with higher initial premiums.
- Monitor Premium Trends: Stay informed about industry trends and potential factors that could affect premiums, such as healthcare inflation or changes in insurance regulations.
Claim Denials
Claim denials are a concern for any type of insurance, including long-term care.
While insurers strive to process claims fairly, there may be instances where a claim is denied due to policy limitations or eligibility criteria.
To mitigate this risk:
- Understand Exclusions and Limitations: Carefully review your policy’s exclusions and limitations, such as pre-existing conditions or specific care services not covered.
- Maintain Accurate Records: Keep thorough records of your health history, medical treatments, and care needs to support your claim.
- Consult with an Insurance Professional: If your claim is denied, seek guidance from an insurance professional or a qualified attorney to understand your options and potential recourse.
Resources and Support for Consumers
Navigating the world of long-term care insurance can be daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. There are several resources available to help you make informed decisions.
Reputable Sources for Research
The process of choosing a long-term care insurance policy can be complex. To ensure you make informed decisions, it’s crucial to consult reputable sources for information and guidance.
- The National Council on Aging (NCOA): The NCOA offers comprehensive resources on long-term care planning, including information on insurance, alternatives, and financial planning. They also provide a free, online long-term care insurance calculator to help you estimate potential costs.
- The American Association for Long-Term Care Insurance (AALTCI): This organization provides information and resources for consumers, including a directory of certified long-term care insurance agents and brokers. They also offer educational materials and webinars on various aspects of long-term care planning.
- The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): The NAIC is a non-profit organization that oversees state insurance regulators. Their website provides information on long-term care insurance, including state-specific regulations and consumer protection tips.
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): CMS administers the Medicare and Medicaid programs and offers information on long-term care services, including coverage options and eligibility requirements.
- State Insurance Departments: Each state has an insurance department that regulates insurance companies and provides consumer protection. Their websites offer information on long-term care insurance, including licensed insurance agents and brokers in your state.
Finding a Qualified Insurance Agent or Broker
A qualified insurance agent or broker can be a valuable resource in your long-term care planning journey. They can help you understand your needs, compare different policy options, and find the best fit for your individual circumstances.
- Look for Certified Agents: The AALTCI offers a certification program for long-term care insurance agents. Look for agents who are certified by the AALTCI or have significant experience in long-term care insurance.
- Seek Recommendations: Ask friends, family, or financial advisors for recommendations. You can also check online directories for insurance agents in your area.
- Check Credentials: Ensure the agent or broker is licensed in your state and has a good reputation. You can check their credentials on the NAIC’s website or your state insurance department’s website.
- Ask Questions: Before committing to an agent or broker, ask them about their experience, qualifications, and fees. Make sure you understand their role and how they will assist you.
Consumer Education and Support Services
Several organizations offer consumer education and support services to help you navigate the complexities of long-term care planning.
- The National Long-Term Care Ombudsman Program: This program provides assistance to individuals and their families who are receiving long-term care services. They can help resolve complaints, advocate for better care, and provide information on consumer rights.
- The Eldercare Locator: This service, run by the Administration for Community Living, provides information and referrals to resources for older adults and their families. They can help you find long-term care services in your area, including home care, assisted living, and nursing homes.
- The National Council on Aging (NCOA): The NCOA offers various programs and resources to help older adults and their families plan for long-term care. They also provide counseling and support services.
The Future of Long-Term Care Insurance
The long-term care insurance market is undergoing significant changes, driven by evolving healthcare needs, demographic shifts, and technological advancements. These factors are reshaping the industry landscape and presenting both challenges and opportunities for insurers and consumers alike.
Impact of Healthcare Reform and Aging Demographics
The aging population is a major driver of the growing demand for long-term care services. The number of Americans aged 65 and older is projected to more than double by 2060, leading to a significant increase in the need for long-term care. This demographic shift, coupled with healthcare reform initiatives, is influencing the long-term care insurance market in several ways.
- Increased demand for coverage: As the population ages, the demand for long-term care insurance is expected to rise. Individuals are becoming increasingly aware of the financial burden associated with long-term care, and many are seeking insurance protection.
- Shifting care models: Healthcare reform is promoting a shift towards community-based care models, such as home health services and assisted living facilities. This shift is influencing the types of long-term care benefits offered by insurance companies.
- New payment models: The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has introduced new payment models for healthcare services, including bundled payments and accountable care organizations (ACOs). These models are designed to improve care coordination and reduce costs, which could impact the pricing and availability of long-term care insurance.
Final Wrap-Up
Navigating the intricacies of long-term care insurance requires careful consideration and a proactive approach. By understanding the fundamentals, exploring different options, and engaging with reputable companies, you can make informed decisions that protect your financial future and provide peace of mind during a potentially challenging time. Remember, seeking professional advice from a qualified insurance agent or broker can be invaluable in navigating this complex landscape.